EXOSOME
EXOSOME OVERVIEW
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles with a diameter of 40-160nm released by cells.
Exosomes form within endosomal compartments inside cells before being secreted.
Exosomes contain proteins, lipids, metabolites, and nucleic acids from parent cells.
Exosomes can transfer molecular cargo between cells to influence recipient cell function.
What are ExoCell
APPLICATION IN HEALTH
Tissue Repair and Regeneration: Exosome therapy holds promise for aiding tissue repair and regeneration in damaged tissues or organs.
Reducing Inflammation: Exosomes contain anti-inflammatory molecules that can help reduce inflammation in conditions like arthritis.
Wound Healing: Exosomes can promote faster and more effective wound healing through their effects on cell communication and tissue repair.
Anti-Aging Effects: Exosomes may rejuvenate skin cells and aid in reducing signs of aging.
Orthopedic Applications: Exosome therapy is being explored to aid recovery from injuries affecting joints, tendons, or cartilage.
Exosomes in Joint Growth: When exosomes are extracted from the body and injected into damaged joints, they can increase cellular division and growth activities. This allows injured joints to rapidly repair themselves within a short period and transform into healthy joints.
Neurological Disorders: Exosomes may promote nerve regeneration and reduce inflammation in conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, or stroke.
SKIN CARE
Exosome Therapy for Skin Rejuvenation
Exosome therapy is emerging as a revolutionary approach in the realm of skincare, leveraging the power of cellular communication to enhance skin health and appearance. Here’s how exosomes are making waves in skincare:
Cellular Communication:
Exosomes as Messengers: Exosomes serve as cellular couriers, delivering essential growth factors, proteins, and genetic materials to skin cells. This facilitates intercellular communication, enhancing the skin’s natural repair and regeneration processes.
Stimulating Regeneration: Packed with signaling molecules, exosomes can stimulate skin cells to rejuvenate and repair, promoting the renewal of the skin’s outer layers for a more youthful appearance.
Anti-inflammatory Properties: The inherent anti-inflammatory capabilities of exosomes can help mitigate inflammation within the skin, addressing a root cause of aging and skin conditions such as acne and rosacea.
Enhancing Blood Supply: By promoting angiogenesis, exosomes improve blood flow to the skin, ensuring that cells receive the oxygen and nutrients needed for optimal health and function.
Methods of Administration:
Injection: For targeted rejuvenation, exosomes can be directly injected into specific areas of the skin. This method ensures that the exosomes efficiently reach the deeper layers of the skin where they can exert their regenerative effects.
Topical Application: Advances in formulation technology are enabling the development of creams and serums infused with exosomes. These topical products aim to penetrate the skin’s surface, delivering exosomes to the deeper layers for enhanced repair and rejuvenation.
Treatment Protocol:
Clinical Procedure: Administered by a dermatologist or skincare specialist, exosome therapy is performed in a clinical setting to ensure precision and safety.
Preparation: Areas of the skin targeted for treatment may be numbed to ensure comfort during the procedure.
Application: Whether through injections or topical application, the exosome solution is carefully applied to the skin, focusing on areas needing rejuvenation or repair.
Customized Treatment: The treatment plan, including the number of sessions and the concentration of exosomes, is tailored to the individual’s skin condition and goals.
Mechanism of Action:
Regenerative Effects: Upon administration, exosomes release their cargo into the skin cells, stimulating processes such as cell turnover, collagen production, and tissue repair. This can lead to improved skin texture, elasticity, and overall appearance.
Promoting Skin Health: The actions of exosomes can create a healthier skin environment, reducing signs of aging, and addressing specific skin concerns such as dryness, fine lines, and uneven tone.
Exosome therapy represents a cutting-edge addition to the arsenal of skincare treatments, offering a novel way to harness the body’s own regenerative capabilities for skin rejuvenation. As research progresses, exosome therapy holds promise for transforming skincare practices and outcomes.
Exosome Therapy for Skin Rejuvenation
Exosome therapy is emerging as a revolutionary approach in the realm of skincare, leveraging the power of cellular communication to enhance skin health and appearance. Here’s how exosomes are making waves in skincare:
Cellular Communication:
Exosomes as Messengers: Exosomes serve as cellular couriers, delivering essential growth factors, proteins, and genetic materials to skin cells. This facilitates intercellular communication, enhancing the skin’s natural repair and regeneration processes.
Stimulating Regeneration: Packed with signaling molecules, exosomes can stimulate skin cells to rejuvenate and repair, promoting the renewal of the skin’s outer layers for a more youthful appearance.
Anti-inflammatory Properties: The inherent anti-inflammatory capabilities of exosomes can help mitigate inflammation within the skin, addressing a root cause of aging and skin conditions such as acne and rosacea.
Enhancing Blood Supply: By promoting angiogenesis, exosomes improve blood flow to the skin, ensuring that cells receive the oxygen and nutrients needed for optimal health and function.
Methods of Administration:
Injection: For targeted rejuvenation, exosomes can be directly injected into specific areas of the skin. This method ensures that the exosomes efficiently reach the deeper layers of the skin where they can exert their regenerative effects.
Topical Application: Advances in formulation technology are enabling the development of creams and serums infused with exosomes. These topical products aim to penetrate the skin’s surface, delivering exosomes to the deeper layers for enhanced repair and rejuvenation.
Treatment Protocol:
Clinical Procedure: Administered by a dermatologist or skincare specialist, exosome therapy is performed in a clinical setting to ensure precision and safety.
Preparation: Areas of the skin targeted for treatment may be numbed to ensure comfort during the procedure.
Application: Whether through injections or topical application, the exosome solution is carefully applied to the skin, focusing on areas needing rejuvenation or repair.
Customized Treatment: The treatment plan, including the number of sessions and the concentration of exosomes, is tailored to the individual’s skin condition and goals.
Mechanism of Action:
Regenerative Effects: Upon administration, exosomes release their cargo into the skin cells, stimulating processes such as cell turnover, collagen production, and tissue repair. This can lead to improved skin texture, elasticity, and overall appearance.
Promoting Skin Health: The actions of exosomes can create a healthier skin environment, reducing signs of aging, and addressing specific skin concerns such as dryness, fine lines, and uneven tone.
Exosome therapy represents a cutting-edge addition to the arsenal of skincare treatments, offering a novel way to harness the body’s own regenerative capabilities for skin rejuvenation. As research progresses, exosome therapy holds promise for transforming skincare practices and outcomes.
Exosome Therapy for Skin Rejuvenation
Exosome therapy is emerging as a revolutionary approach in the realm of skincare, leveraging the power of cellular communication to enhance skin health and appearance. Here’s how exosomes are making waves in skincare:
Cellular Communication:
Exosomes as Messengers: Exosomes serve as cellular couriers, delivering essential growth factors, proteins, and genetic materials to skin cells. This facilitates intercellular communication, enhancing the skin’s natural repair and regeneration processes.
Stimulating Regeneration: Packed with signaling molecules, exosomes can stimulate skin cells to rejuvenate and repair, promoting the renewal of the skin’s outer layers for a more youthful appearance.
Anti-inflammatory Properties: The inherent anti-inflammatory capabilities of exosomes can help mitigate inflammation within the skin, addressing a root cause of aging and skin conditions such as acne and rosacea.
Enhancing Blood Supply: By promoting angiogenesis, exosomes improve blood flow to the skin, ensuring that cells receive the oxygen and nutrients needed for optimal health and function.
Methods of Administration:
Injection: For targeted rejuvenation, exosomes can be directly injected into specific areas of the skin. This method ensures that the exosomes efficiently reach the deeper layers of the skin where they can exert their regenerative effects.
Topical Application: Advances in formulation technology are enabling the development of creams and serums infused with exosomes. These topical products aim to penetrate the skin’s surface, delivering exosomes to the deeper layers for enhanced repair and rejuvenation.
Treatment Protocol:
Clinical Procedure: Administered by a dermatologist or skincare specialist, exosome therapy is performed in a clinical setting to ensure precision and safety.
Preparation: Areas of the skin targeted for treatment may be numbed to ensure comfort during the procedure.
Application: Whether through injections or topical application, the exosome solution is carefully applied to the skin, focusing on areas needing rejuvenation or repair.
Customized Treatment: The treatment plan, including the number of sessions and the concentration of exosomes, is tailored to the individual’s skin condition and goals.
Mechanism of Action:
Regenerative Effects: Upon administration, exosomes release their cargo into the skin cells, stimulating processes such as cell turnover, collagen production, and tissue repair. This can lead to improved skin texture, elasticity, and overall appearance.
Promoting Skin Health: The actions of exosomes can create a healthier skin environment, reducing signs of aging, and addressing specific skin concerns such as dryness, fine lines, and uneven tone.
Exosome therapy represents a cutting-edge addition to the arsenal of skincare treatments, offering a novel way to harness the body’s own regenerative capabilities for skin rejuvenation. As research progresses, exosome therapy holds promise for transforming skincare practices and outcomes.
TREATING HAIR LOSS
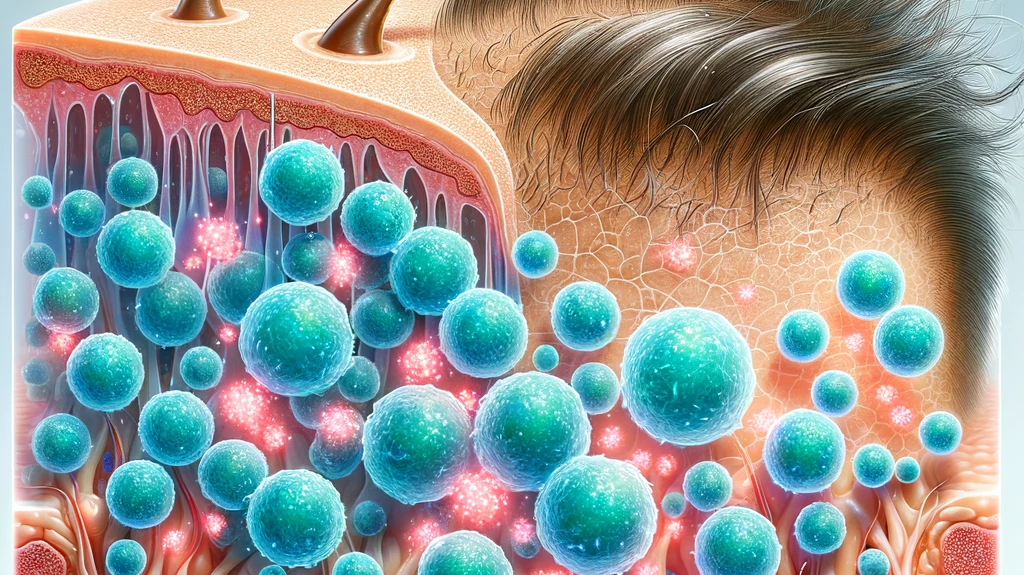
Cellular Communication: Exosomes act as messengers, carrying growth factors, proteins, and genetic materials to hair follicles, facilitating communication and promoting repair processes.
Stimulating Growth: They contain key signals that can awaken dormant hair follicles, encouraging the transition from the telogen (resting) phase to the anagen (growth) phase.
Anti-inflammatory Properties: Exosomes have inherent anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce scalp inflammation, a common contributing factor to hair loss.
Promoting Blood Supply: By enhancing angiogenesis, exosomes help improve blood flow to the scalp, providing follicles with the necessary nutrients and oxygen for hair growth.
Methods of administration
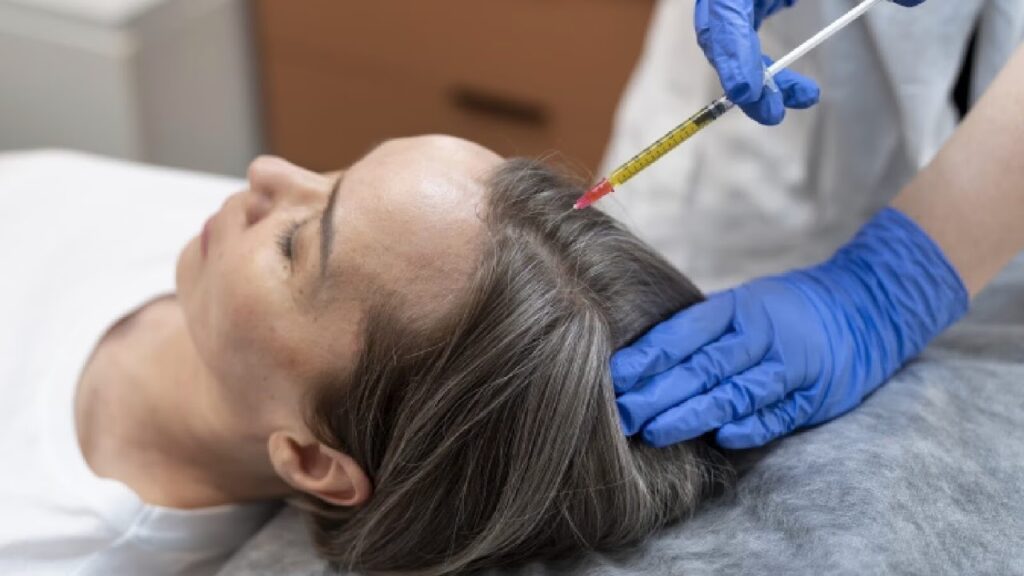
Injection: The most common method of administering exosomes for hair loss is through direct injection into the scalp. This localized delivery aims to ensure that the exosomes reach the hair follicles where they can exert their effects.
Topical Application: Research is ongoing into formulations that allow exosomes to be applied topically to the scalp in a cream or serum form. However, the challenge with topical application is ensuring that the exosomes penetrate deeply enough to reach the hair follicles.
Treatment Protocol
A healthcare provider, often a dermatologist or a specialist in regenerative medicine, typically performs the procedure in a clinical setting.
The scalp area targeted for treatment is usually numbed with a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort.
The exosome solution is then carefully injected into multiple sites across the scalp, focusing on areas of thinning or hair loss.
The number of sessions and the total volume of exosomes administered can vary based on the individual’s condition and the treatment protocol.
Mechanism of Action
Once administered, the exosomes are believed to release their cargo of growth factors, cytokines, and other bioactive molecules that can stimulate hair follicle cells, promote angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and modulate the immune response in the scalp.
These actions can potentially create a more favorable environment for hair growth and regeneration.
EXOSOME IN CANCER
Exosomes have begun to be explored as vehicles for carrying therapeutic payloads, such as short interfering RNA, chemotherapeutics, or CRISPR-Cas9 for genome editing. They have been shown to improve survival in animal models of pancreatic cancer by targeting the oncogenic KRAS gene. This indicates potential for exosomes in cancer therapy, though the mechanisms governing their targeting of specific cells and tissues remain an area of ongoing research.
Importance of ExoCell
Unlocking Regenerative Potentials, ExoCell stands at the forefront of skincare innovation, harnessing the power of HUMSC-derived exosomes to deliver transformative benefits for your skin.
Cellular Rejuvenation
The bioactive molecules within ExoCell dive deep into cellular structures, promoting rejuvenation at the core. Stimulating cellular turnover, this formulation contributes to fresher, more youthful-looking skin.
Collagen Synthesis
Experience the magic of collagen synthesis. ExoCell is designed to stimulate the production of this vital protein, enhancing skin elasticity, firmness, and resilience. Say hello to visibly smoother and plumper skin.

Antioxidant Defense
Protect your skin against oxidative stress with ExoCell's antioxidant-rich composition. Guarding against environmental aggressors, this formulation aids in maintaining skin health and vitality.
Benefits & Applications
At GainMed, seize the authority to transform your health through the Benefits and Applications of Stem Cells. Empowered by groundbreaking research and cutting-edge technology, our stem cell therapies offer a decisive path to optimal well-being. Whether you aspire to rejuvenate tissues, enhance recovery from injuries, or address chronic conditions, our treatments encompass a spectrum of applications with proven benefits
Cellular Renewal
Visible Radiance and Health
Enhanced Collagen Synthesis
Enhanced brain health
Skin rejuvenation
Faster healing
Get In Touch
+1 720 755 5555
Address 23101 Lake center Dr, Ste 315, Lakr Forest, 92630
Email: info@gainbiomed.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Most frequent questions and answers
Stem cell therapies are utilized for a range of conditions, including but not limited to orthopedic issues, neurological disorders, blood disorders, and cosmetic enhancements. Each treatment plan is tailored to the specific needs of the individual.
Yes, when conducted by qualified professionals in a controlled and sterile environment, stem cell procedures are generally considered safe. The use of autologous stem cells (derived from the patient's own body) minimizes the risk of rejection or adverse reactions.
The recovery process varies depending on the type of procedure. In many cases, patients experience minimal downtime as stem cell therapies often involve minimally invasive approaches. Post-procedure care typically includes a tailored rehabilitation plan to optimize healing and recovery.

